Introduction
Solar energy, derived from the sun’s radiation, is one of the most promising and abundant renewable energy sources available to humanity. This energy is harnessed through various technologies, primarily photovoltaic (PV) panels and solar thermal systems. The quest for sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions has led to a significant increase in solar energy adoption worldwide. This journal explores the multifaceted aspects of solar energy, including its principles, technologies, applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
The Science Behind Solar Energy
Solar energy is essentially the radiant light and heat from the sun that reaches the Earth. This energy can be converted into usable forms of power through several methods:
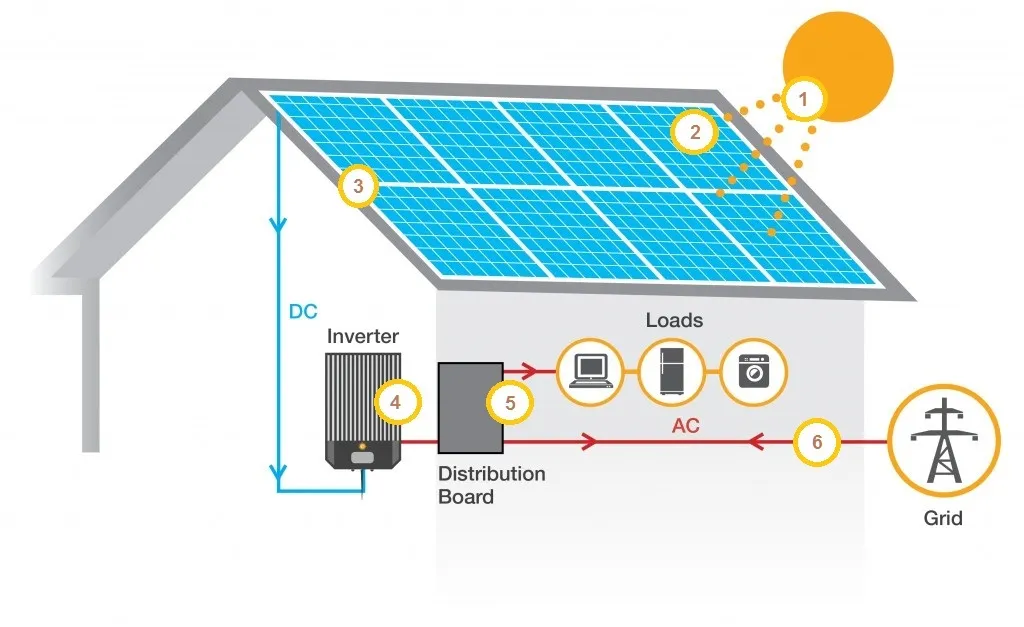
- Photovoltaic (PV) Cells: PV cells, commonly known as solar panels, convert sunlight directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the PV cells, it excites electrons in the semiconductor material, typically silicon, creating an electric current.
- Solar Thermal Systems: These systems harness solar energy to generate heat. Solar thermal collectors capture and concentrate sunlight to heat a fluid, which can then be used to produce steam and drive a turbine to generate electricity or provide direct heating.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a small area. The concentrated light is then used as a heat source for a conventional power plant. CSP systems are typically used in large-scale solar farms.

Applications of Solar Energy
Solar energy has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large-scale industrial plants:
- Residential Use: Homeowners can install rooftop solar panels to generate electricity for their homes. Solar water heaters are also popular for providing hot water.
- Commercial and Industrial Use: Businesses and factories can use large solar installations to reduce their electricity costs and carbon footprint. Solar energy can power everything from office buildings to manufacturing plants.
- Utility-Scale Solar Farms: These large-scale installations, often spread over hundreds of acres, generate substantial amounts of electricity that can be fed into the grid to supply power to a large number of homes and businesses.
- Off-Grid Applications: In remote areas without access to the electrical grid, solar energy provides a reliable and sustainable power source. Solar-powered irrigation systems, lighting, and communication devices are examples of off-grid applications.
- Transportation: Solar energy is being integrated into transportation through solar-powered vehicles and solar charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs). Solar panels can also be used in aviation, as seen in solar-powered aircraft.
Benefits of Solar Energy
The advantages of solar energy are numerous, making it a crucial component of the global transition to sustainable energy:
- Renewable and Abundant: Solar energy is virtually inexhaustible, with the sun expected to shine for another 5 billion years. It is available almost everywhere on Earth, making it a reliable energy source.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar energy generation produces no greenhouse gases or air pollutants, significantly reducing the environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. It helps mitigate climate change and improves air quality.
- Economic Benefits: The cost of solar technology has been decreasing rapidly, making it more affordable for consumers and businesses. Solar installations create jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Energy Independence: By harnessing solar energy, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and economic stability.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, solar panels require minimal maintenance and have no fuel costs, resulting in low operating expenses over their lifespan.
Challenges of Solar Energy
Despite its numerous benefits, solar energy faces several challenges that need to be addressed:
- Intermittency: Solar energy generation is dependent on sunlight, which varies with weather conditions and time of day. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, are required to provide a consistent power supply.
- Initial Costs: The upfront cost of solar installations can be high, although this is offset by long-term savings. Incentives and subsidies are often necessary to make solar energy more accessible.
- Space Requirements: Large-scale solar farms require significant land areas, which can be a constraint in densely populated regions. Innovative solutions, such as floating solar farms, are being explored to address this issue.
- Energy Storage: Efficient and affordable energy storage systems are essential to store excess energy generated during sunny periods for use during cloudy periods or at night. Advances in battery technology are crucial for the future of solar energy.
- Grid Integration: Integrating a high proportion of solar energy into existing electrical grids requires upgrades and modifications to ensure stability and reliability. Smart grid technologies and demand response mechanisms are important in this regard.
Future Prospects
The future of solar energy looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increased global commitment to renewable energy. Key trends and innovations include:
- Advanced PV Technologies: Research is focused on developing more efficient and cost-effective PV materials, such as perovskite solar cells, which have the potential to surpass traditional silicon cells in efficiency and affordability.
- Bifacial Solar Panels: These panels can capture sunlight on both sides, increasing energy yield and making them suitable for various environments and applications.
- Solar Integration with Smart Grids: The integration of solar energy with smart grid technologies enhances grid stability, efficiency, and resilience. Smart grids can dynamically manage energy flow, storage, and distribution.
- Energy Storage Innovations: Advances in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries, promise to improve energy storage capacity, efficiency, and lifespan.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining solar energy with other renewable sources, such as wind and hydropower, can provide a more reliable and balanced energy supply.
- Solar Desalination: Solar energy can be used to desalinate seawater, providing a sustainable solution to freshwater scarcity in arid regions.
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Integrating solar panels into building materials, such as windows and facades, allows for the seamless incorporation of solar energy generation into urban environments.

Conclusion
Solar energy is a key player in the global transition to a sustainable and low-carbon future. Its potential to provide clean, abundant, and affordable energy makes it an essential component of the world’s energy portfolio. While challenges remain, continued innovation and supportive policies are paving the way for broader adoption and integration of solar energy into our daily lives. As we move forward, solar energy will play a pivotal role in addressing climate change, enhancing energy security, and fostering economic development.

